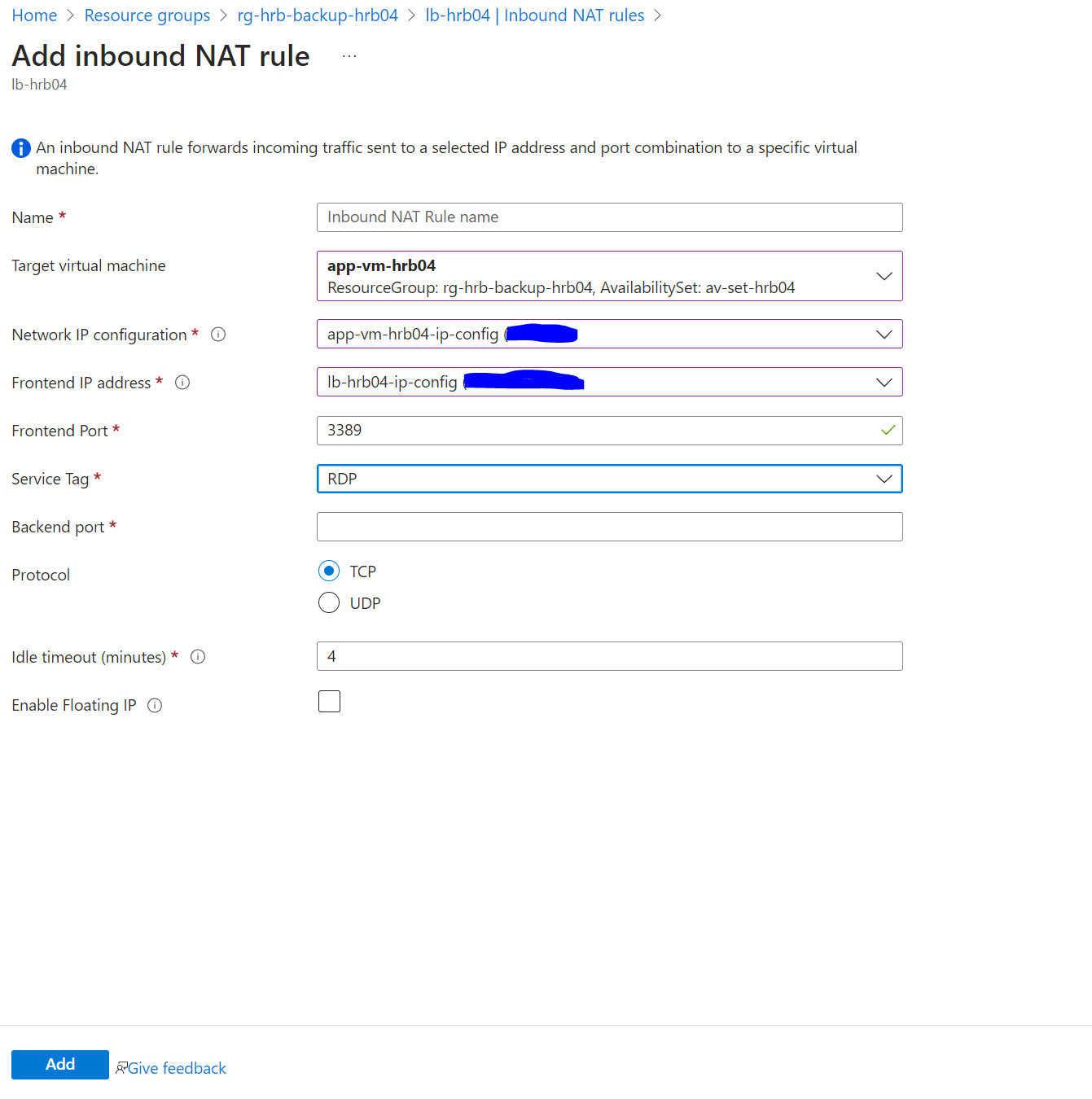
In Azure portal LB inbound NAT rule is created via the following form, where I see a property for target VM and port
Is there a way to specify LB NAT rule target VM via Azure CLI or Terraform?
In Terraform, I see there only an approach to create rule and attach it to the network interface of VM via separate resource, but it does not feet my case and more over as I tested it haven’t worked out
So is there a way to perform exactly an action in Terraform or Azure CLI to create NAT rule as we do via Azure Portal UI?




2
Answers
Created load balancer and added two virtual machines in backend pool:
You could identify the target VM using Network interfaces. There is no explicit comment to specify the target VM of the LB NAT rule.
Created NAT rule and to check the target vm make use of below command using CLI.
Now, target virtual machine of network interface as shown below in this way you can identify specific vm of load balancer:
In portal:
Reference:
az network lb inbound-nat-rule | Microsoft Learn
This functionality is possible in CLI. You will need to create an inbound NAT rule and then do a PUT NIC call to reference the nat rule to the VM (see example below).
Example:
This command will create an inbound NAT rule without any target VM or backend pool.
Refer: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/network/lb/inbound-nat-rule?view=azure-cli-latest#az-network-lb-inbound-nat-rule-create
This command will add the above created inbound NAT rule to a target VM that you specify.
Refer: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/network/nic/ip-config/inbound-nat-rule?view=azure-cli-latest#az-network-nic-ip-config-inbound-nat-rule-add
The Manage inbound NAT rules for Azure Load Balancer document doesn’t seem to reflect this information. I will contact the doc author to update our docs to make this clearer.