In Azure SQL database, the same query is completed in 4 seconds when Row Level Security is active, and in 1 second when Row Level Security is disabled.
When I compared the execution plans of the queries, I found that the optimizer could not use parallelism when Row Level Security was active. You can see the below screenshot.
My questions are;
1- Is it technically possible for the optimizer to use parallelism when Row Level Security is active?
2- If possible, what should I do to make the optimizer use parallelism even when Row Level Security is active?




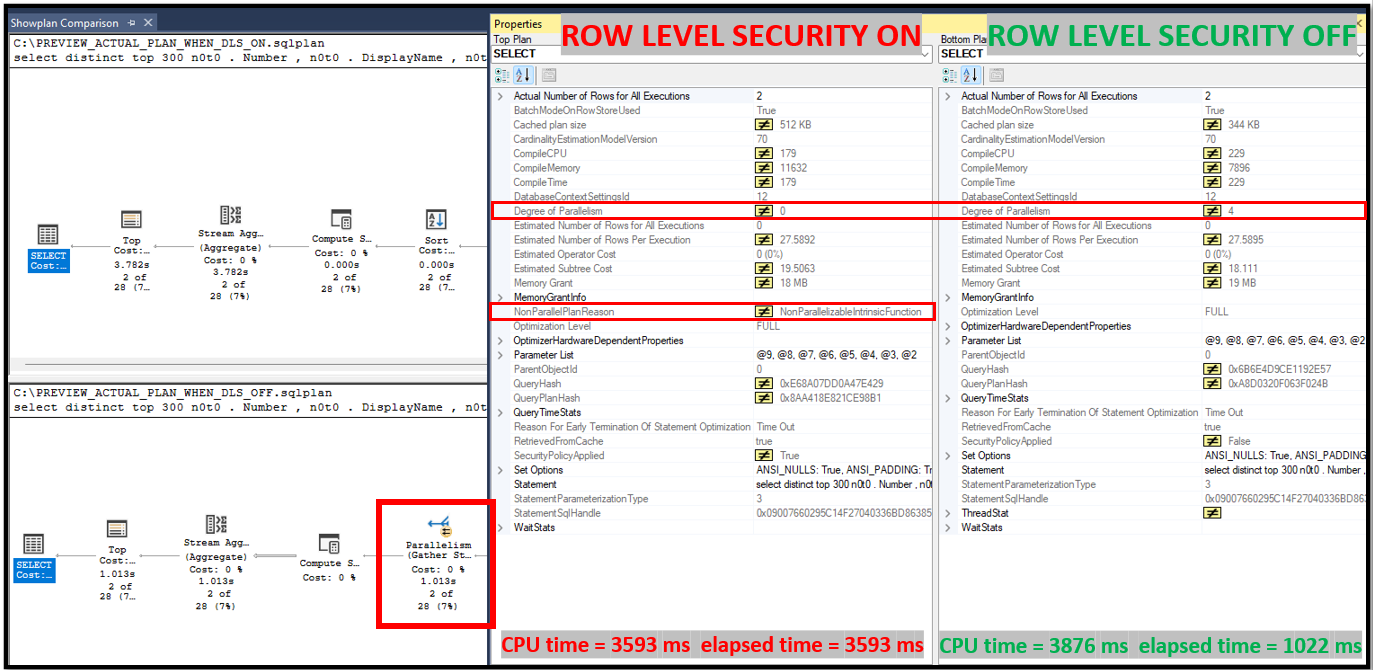
2
Answers
Thank you very much for the document you shared.
The following comment in the document was very helpful in understanding the problem.
"The reason for not using parallelism is not row-level security by itself, but rather a specific function that was used in the security policy. Readers might think that row-level security by itself can block parallelism, but this is not true. The "important lesson here is to write the security policy in a way that allows parallelism."
After a while I learned that we use Row-Level Security through a function that uses SESSION_CONTEXT().
Microsoft does not allow parallelism on Azure DBs when SESSION_CONTEXT is used in any function (it is not limited to RowLevelSecurity).
Hope it will be very useful for anyone who will face same issue.
Kind Regards.
This is a known issue documented here. The culprit is maybe the way the function used by the security policy was built. To avoid this, try to use simple and deterministic filter predicates that do not involve complex calculations or joins with other tables.
A workaround may be to try using MAXDOP query hint (OPTION(MAXDOP 2)) but the article suggested that method and others did not work. Hope this method work in your scenario or one of the workarounds Microsoft Support tried.