EDIT: The dash size of 10 in the code sample is arbitrary. The dash size is whatever looks good.
Let’s say in SwiftUI, you want to have a custom list item that has a dotted outline — to serve as a "add item hint."
So you use a strokeBorder like this:
struct ContentView: View {
let items:[String] = ["a","b","c"]
@State var itemsEmpty = false
var body: some View {
Text("toggle").onTapGesture {
itemsEmpty.toggle()
}
VStack {
Spacer()
if !itemsEmpty {
List{
ForEach(items, id: .self) {item in
Text(item)
}
}
} else {
// The "list item hint" view
List{
Text("ADD")
.listRowBackground(
RoundedRectangle(cornerSize: CGSize(width: 15, height: 15))
.strokeBorder(style: StrokeStyle(lineWidth: 4, dash: [10]))
)
}
}
Spacer()
}
.padding()
}
}
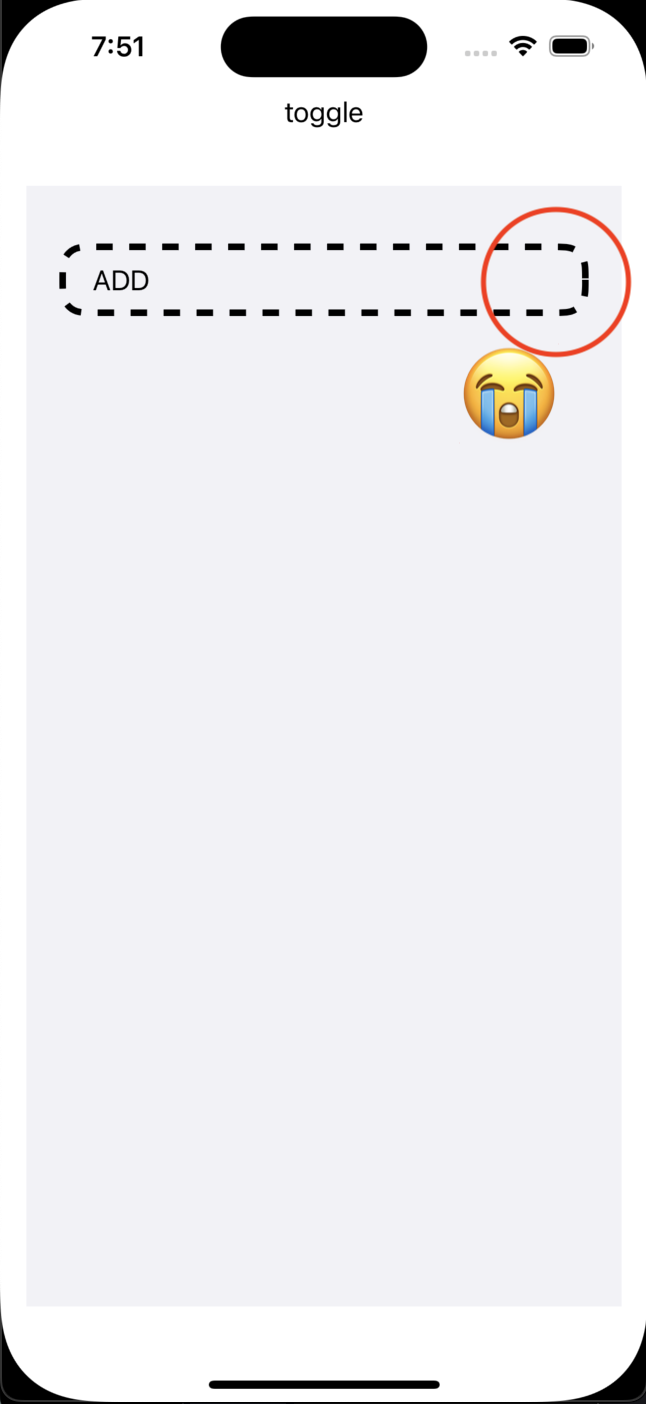
Which results in this:
This same technique is used in this Apple sample, but it is unsatisfactory to me because the lines (understandably) are not evenly distributed and we get a nasty truncation at the wrap-around point.
The only (also unsatisfactory) ways I can think of to solve this are:
A) To create the view using two mirrored shapes instead… (but this will still result in truncation… only it will be symmetrical trunctation this time).
B) Making some kind of "sun rays" radial gradient and stack two rounded rectangles in a way that gives the illusion that we have a dotted outline… (but the "heads and tails" of these lines will not be perpendicular to the outline path because the "sun rays" all originate at a single point)
C) Using the parametric equation for a squircle (squircle because a superellipse looks like crap IMO if it is rectangular) (which would need to be cut in half and stretched like limo) and creating a path from it, then drawing the dashes as intermittent lines along that path using t = 2 * (pi) / some divisor to establish the resolution. The trouble with this is that the modified (limo-fied) shape would be a piecewise function and therefore cannot be driven by t. Also even if it could be, the dashes would not be regular in size for somewhat obvious reasons I can’t put into words.
How can this be done??




2
Answers
For anyone interested...
This is an alternate re-usable version where instead of defining a desired dash length, we set a desired number of dashes.
It also prevents a problematic odd number of dashes.
The dash will not be truncated if the length of the stroke (perimeter of the shape) is a integer multiple of the dash size.
Therefore, you need to dynamically adjust the dash size according to the perimeter. See this and this for finding the arc length of parametric and non-parametric curves respectively. If this is too difficult to integrate, also consider calculating the lengths of each
CGPathElements in the underlyingCGPathfor the shape. See this gist (though it’s written in Swift 2), or this repo for how to do this.In the case of the rounded rectangle with a corner radius, you can simply add up the lengths of the straight parts and the circular parts.
Example output: