I have a Kubernetes cluster with ingress-nginx. We use Azure DNS zone with a record for *.domain1.com that points all traffic to our ingress controller.
I need to make sure that our cluster do not serve invalid certificates when someone requests host that doesn’t exist in the cluster.
We have wildcard certificates for *.domain1.com, *.dev.domain1.com etc., but since we can get traffic for any nested sub-subdomain like https://super.fake.dev.domain1.com we can’t have a certificate for double wildcard hosts: *.*.dev.domain1.com
I thought that a solution would be to redirect all traffic that did not match any host in any Ingress to some website, lets say https://google.com.
I can do that for http traffic, but when I’m trying to the same address using https it fails.
I created an Ingress like this:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: default-redirect
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: |
return 307 https://google.com;
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
defaultBackend:
service:
name: does-not-exist
port:
name: http
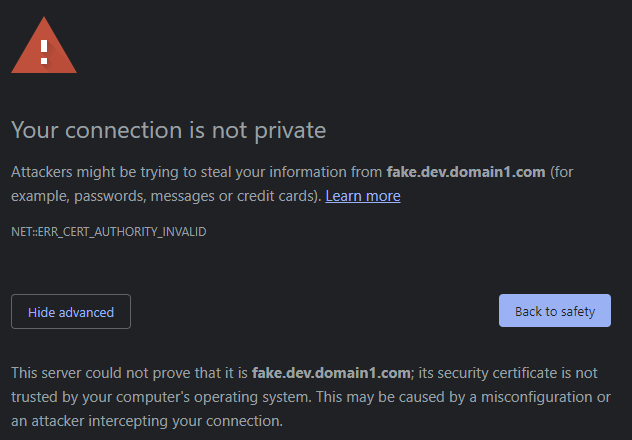
When I open http://fake.dev.domain1.com in Chrome I’m correctly redirected to https://google.com, but when I do the same with https https://fake.dev.domain1.com Chrome shows:
I also tried adding
tls:
- hosts:
- "*.dev.domain1.com"
secretName: default-redirect
But that didn’t change anything (and wouldn’t work anyway because host can be anything in domain1.com)
I can’t use nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/temporal-redirect: https://google.com annotation because it’s ignored when the defaultBackend is selected.
I tried using:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/server-snippet: |
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name ~^.*.domain1.com$;
return 307 https://google.com;
annotation but then the defaultBackend is hit without redirecting and 503 is returned because it doesn’t exist.
I’m not sure what else I can do. Maybe I’m coming to the problem from the wrong angle? Maybe I should fix it somehow on the DNS level?




2
Answers
I don’t think redirecting to google is the right approach.
I’d pick a better http status code to represent the reality of the situation, a 421 perhaps… or a 418 if you wanted to have a laugh.
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Status
Your browser doesn’t recognize the validity of your certificate because your certificate is not valid.
The problem happens only with
HTTPSbecauseHTTPdoesn’t use certificates. Vice versaHTTPSexpects the server to show a certificate, which the client will validate against its known trusted Certificate Authority.You can run
kubectl describe ingress,certificateto understand more about the error.You will need at least one Issuer or ClusterIssuer to begin issuing certificates within your cluster.
So, add the
IssuerKubernetes component:Check the issuer:
Finally, add the issuer in your ingress configuration, under the annotation key:
Check the secrets
kubectl get secretsand the certificateskubectl get certificatesPS: of course you need to validate the domain for which the certificate is being requested to a global Certificate Authority (CA), in case you don’t have already.