I am trying to setup ELK on my Ubuntu (version 22.04). I was able to setup ElasticSearch version 7.17.15
After starting the ElasticSearch service, I tried setting up Kibana by following the below steps:
sudo apt-get install kibana sudo nano /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
and uncommenting the lines server.port: 5601 server.host: "localhost" elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
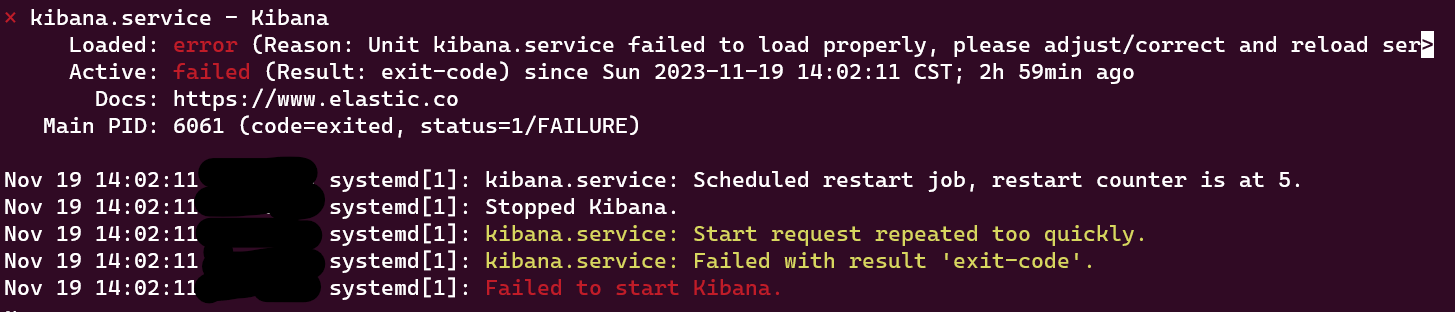
After this,when I try to start the kibana service by running the command sudo systemctl start kibana, I get the error:
Failed to start kibana.service: Unit kibana.service failed to load properly, please adjust/correct and reload service manager: Device or resource busy.
See system logs and ‘systemctl status kibana.service’ for details.
kibana.yml contents
### >>>>>>> BACKUP START: Kibana interactive setup (2023-11-20T00:00:42.632Z)
# For more configuration options see the configuration guide for Kibana in
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/index.html
# =================== System: Kibana Server ===================
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use.
server.port: 5601
# Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values.
# The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect.
# To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address.
server.host: "localhost"
# Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy.
# Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath
# from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup.
# This setting cannot end in a slash.
#server.basePath: ""
# Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with
# `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy.
# Defaults to `false`.
#server.rewriteBasePath: false
# Specifies the public URL at which Kibana is available for end users. If
# `server.basePath` is configured this URL should end with the same basePath.
#server.publicBaseUrl: ""
# The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests.
#server.maxPayload: 1048576
# The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes.
#server.name: "your-hostname"
# =================== System: Kibana Server (Optional) ===================
# Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively.
# These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser.
#server.ssl.enabled: false
#server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt
#server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key
# =================== System: Elasticsearch ===================
# The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries.
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
# If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide
# the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana
# index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which
# is proxied through the Kibana server.
#elasticsearch.username: "kibana_system"
#elasticsearch.password: "pass"
# Kibana can also authenticate to Elasticsearch via "service account tokens".
# Service account tokens are Bearer style tokens that replace the traditional username/password based configuration.
# Use this token instead of a username/password.
# elasticsearch.serviceAccountToken: "my_token"
# Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of
# the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting.
#elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500
# Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value
# must be a positive integer.
#elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000
# The maximum number of sockets that can be used for communications with elasticsearch.
# Defaults to `Infinity`.
#elasticsearch.maxSockets: 1024
# Specifies whether Kibana should use compression for communications with elasticsearch
# Defaults to `false`.
#elasticsearch.compression: false
# List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side
# headers, set this value to [] (an empty list).
#elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ]
# Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten
# by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration.
#elasticsearch.customHeaders: {}
# Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable.
#elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000
# =================== System: Elasticsearch (Optional) ===================
# These files are used to verify the identity of Kibana to Elasticsearch and are required when
# xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication in Elasticsearch is set to required.
#elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt
#elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key
# Enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate
# authority for your Elasticsearch instance.
#elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ]
# To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'.
#elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full
# =================== System: Logging ===================
# Set the value of this setting to off to suppress all logging output, or to debug to log everything. Defaults to 'info'
#logging.root.level: debug
# Enables you to specify a file where Kibana stores log output.
#logging:
# appenders:
# file:
# type: file
# fileName: /var/log/kibana/kibana.log
# layout:
# type: json
# root:
# appenders:
# - default
# - file
# layout:
# type: json
# Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch.
#logging.loggers:
# - name: elasticsearch.query
# level: debug
# Logs http responses.
#logging.loggers:
# - name: http.server.response
# level: debug
# Logs system usage information.
#logging.loggers:
# - name: metrics.ops
# level: debug
# =================== System: Other ===================
# The path where Kibana stores persistent data not saved in Elasticsearch. Defaults to data
#path.data: data
# Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file.
#pid.file: /run/kibana/kibana.pid
# Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance
# metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000ms.
#ops.interval: 5000
# Specifies locale to be used for all localizable strings, dates and number formats.
# Supported languages are the following: English (default) "en", Chinese "zh-CN", Japanese "ja-JP", French "fr-FR".
#i18n.locale: "en"
# =================== Frequently used (Optional)===================
# =================== Saved Objects: Migrations ===================
# Saved object migrations run at startup. If you run into migration-related issues, you might need to adjust these settings.
# The number of documents migrated at a time.
# If Kibana can't start up or upgrade due to an Elasticsearch `circuit_breaking_exception`,
# use a smaller batchSize value to reduce the memory pressure. Defaults to 1000 objects per batch.
#migrations.batchSize: 1000
# The maximum payload size for indexing batches of upgraded saved objects.
# To avoid migrations failing due to a 413 Request Entity Too Large response from Elasticsearch.
# This value should be lower than or equal to your Elasticsearch cluster’s `http.max_content_length`
# configuration option. Default: 100mb
#migrations.maxBatchSizeBytes: 100mb
# The number of times to retry temporary migration failures. Increase the setting
# if migrations fail frequently with a message such as `Unable to complete the [...] step after
# 15 attempts, terminating`. Defaults to 15
#migrations.retryAttempts: 15
# =================== Search Autocomplete ===================
# Time in milliseconds to wait for autocomplete suggestions from Elasticsearch.
# This value must be a whole number greater than zero. Defaults to 1000ms
#unifiedSearch.autocomplete.valueSuggestions.timeout: 1000
# Maximum number of documents loaded by each shard to generate autocomplete suggestions.
# This value must be a whole number greater than zero. Defaults to 100_000
#unifiedSearch.autocomplete.valueSuggestions.terminateAfter: 100000
### >>>>>>> BACKUP END: Kibana interactive setup (2023-11-20T00:00:42.632Z)
# This section was automatically generated during setup.
#server.port: 5601
#server.host: "localhost"
#elasticsearch.hosts: ['https://172.23.102.190:9200', 'http://localhost:9200']
logging.appenders.file.type: file
logging.appenders.file.fileName: /var/log/kibana/kibana.log
logging.appenders.file.layout.type: json
logging.root.appenders: [default, file]
pid.file: /run/kibana/kibana.pid
elasticsearch.serviceAccountToken: AAEAAWVsYXN0aWMva2liYW5hL2Vucm9sbC1wcm9jZXNzLXRva2VuLTE3MDA0Mzg0NDEzNjA6a0JOampiMGhUYjZncE1oUHdHZlRYUQ
elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [/var/lib/kibana/ca_1700438442626.crt]
xpack.fleet.outputs: [{id: fleet-default-output, name: default, is_default: true, is_default_monitoring: true, type: elasticsearch, hosts: ['https://172.23.102.190:9200'], ca_trusted_fingerprint: 68ee1d5e342ff535a53d81ea9ed4eb3c921887d58faf2180ae84a3c374cccf3e}]
I was expecting that the kibana service would start on port 5601.




2
Answers
There were three things I had to change to fix this.
Typically Kibana runs on port 5601. It seems that there is a resource conflict. Another process may be using the Kibana port 5601? Please try to stop the other process and restart Kibana.